The alluring sphere of tourism amalgamates the therapeutic mixture of discovery, expedition and adventure in every corner of the world, thereby labeling Tourism as something more than just a booming industry. Tourist destinations assume the role of an entryway to cultural absorption, enthralling destinations, and memorable experiences. In other words, it takes up the role of a catalyst that facilitates cultural exchange, economic progress, and environmental conservation of the destination while nurturing a sense of social responsibility in all of us.
Speaking of tourist destinations, it is very important to understand the concurrent hurdles and opportunities that arise along the way of implementing reasonable and resilient development. This is where we are introduced to The Destination Life Cycle Model, coined by Richard Butler in 1980, that acts as a valuable framework of comprehending the developmental trajectory of tourist destinations. This intriguing model showcases the diverse stages that a tourist destination goes through a period of time which involves its growth, decline, and probable transformation. With a thorough understanding of the model destination managers, policymakers, and stakeholders reap the benefits of the same in order to recognize challenges, grasp opportunities, and encourage environmental conservation practices, which eventually causative enduring success of destinations.
A Professional Doctorate in Tourism Management serves as a revitalizing propellent that aids in destination transformation as destinations around the world are rapidly evolving while facing hurdles and opportunities at every step of their development. Having proper knowledge and aptitude to combat the intricacies of each stages is important for sustainable and successful destination management.
In this blog, we will explain the concept of the Destination Life Cycle Model and how a professional doctorate in tourism management can bring forth effective execution of the Destination Life Cycle Model.
The Destination Life Cycle Model
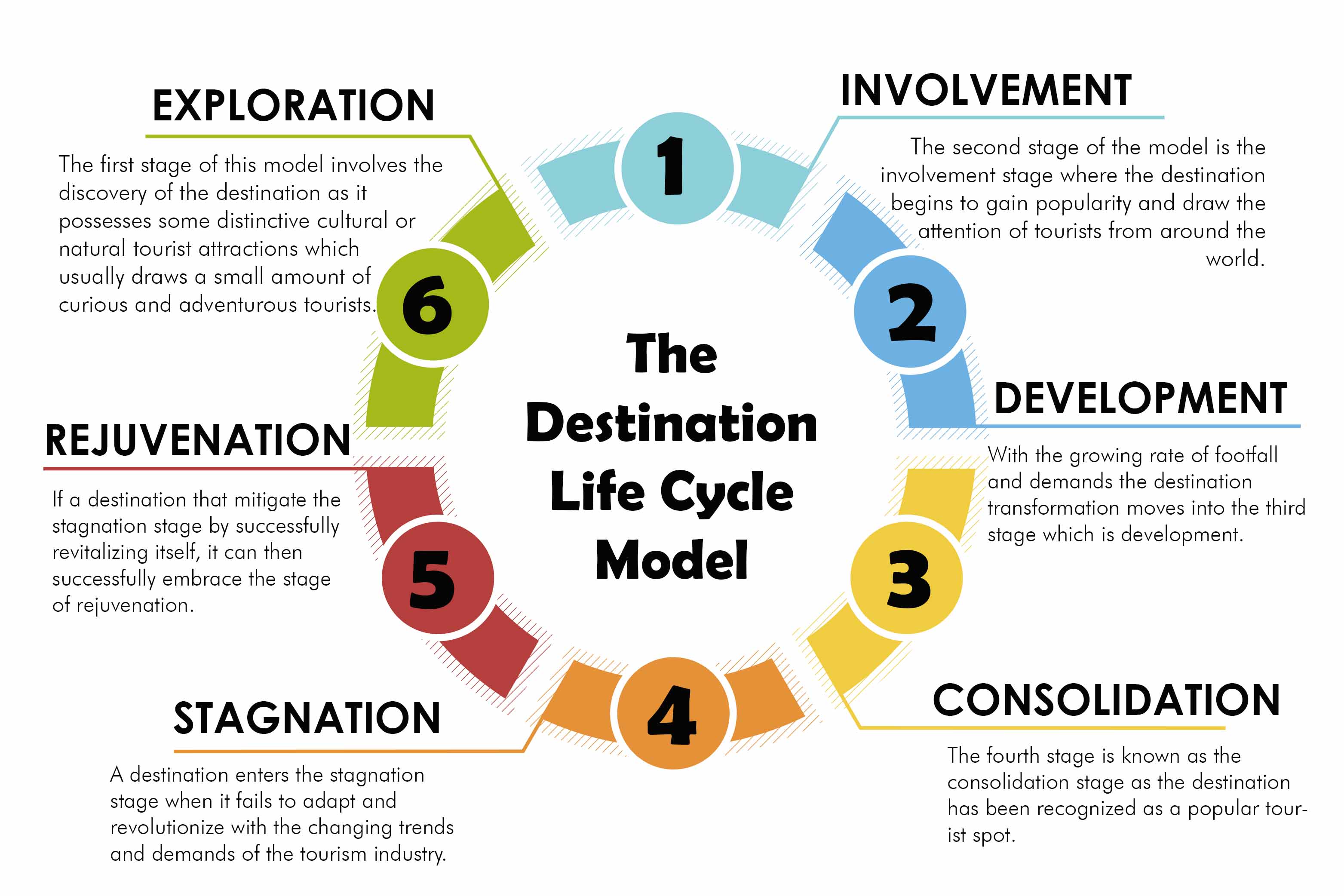
The Destination Life Cycle Model states that a tourist destination goes through six distinct stages:
- Exploration
- Involvement
- Development
- Consolidation
- Stagnation
- Rejuvenation
Each stage represents a phase in the life cycle of a destination and is characterized by specific characteristics, challenges, and opportunities.
- Exploration- The first stage of this model involves the discovery of the destination as it possesses some distinctive cultural or natural tourist attractions which usually draws a small amount of curious and adventurous tourists. It could be a remote island or uninhabited village which due to its exclusivity lack proper tourism services, and local communities are not involved in tourism. In this initial stage it is crucial to safeguard the genuineness and unspoiled nature of the destinations.
- Involvement- The second stage of the model is the involvement stage where the destination begins to gain popularity and draw the attention of tourists from around the world. As the number of tourists increase basic tourism infrastructure and services begin to emerge. Local communities take active part in tourism by offering lodgings, transportation, and other essential amenities.
- Development- With the growing rate of footfall and demands the destination transformation moves into the third stage which is development. This stage involves the rapid development in infrastructure and services to meet the needs of the growing number of tourists. The destination starts gaining worldwide recognition with the expansion of hotels, resorts, and various other local tourist attractions. All these catalyze the growth of the local economy as it creates job and probable investment opportunities. Destinations like well-known coastal cities or historical sites often reach the development stage.
- Consolidation- The fourth stage is known as the consolidation stage as the destination has been recognized as a popular tourist spot. The tourism industry has now become more established and steadier as its main focus has shifted from quantity to quality. Tourism services and facilities are well-developed, and the destination now has international recognition even though safeguarding and preservation of its uniqueness has become a major concern. Many well-known metropolises and cultural locations can be seen in this stage, where maintaining its long-term viability is of utmost importance.
- Stagnation- A destination enters the stagnation stage when it fails to adapt and revolutionize with the changing trends and demands of the tourism industry. This stage is marked by the diminishing number of tourists, obsolete services and facilities along with the lack of investment. In this detrimental stage it is crucial for such destinations to evaluate their fortes and weaknesses and formulate effective strategies to resuscitate their reputation and appeal.
- Rejuvenation -The last stage of the Destination Life Cycle Model is rejuvenation. If a destination that mitigate the stagnation stage by successfully revitalizing itself, it can then successfully embrace the stage of rejuvenation. By addressing the basic problems and formulating effective strategies to boost competitiveness, destinations can reclaim their popularity and attract new market segments.
It is crucial to understand that even though the Destination Life Cycle Model offers a valuable framework for comprehending the progression of tourist destinations, not all destinations follow a linear evolution through the stages. There may be several factors such as political unpredictability, economic predicaments, or natural catastrophes which can disturb the life cycle, causing destinations to skip stages. It should also be noted that the period of each stage is also based on factors such as destination characteristics, market demand, and management strategies.
How does a Professional Doctorate in Tourism Management help with the Destination Life Cycle Model?
A professional doctorate in tourism management can provide valuable knowledge and skills that can greatly assist in understanding and effectively implementing the Destination Life Cycle Model.
- Comprehensive understanding: A Doctorate in Tourism Management imparts a comprehensive understanding of the various stages of the Destination Life Cycle Model.
- All-inclusive knowledge: The program delivers a thorough and all-inclusive knowledge of the aspects influencing each stage, such as economic, social, cultural, and environmental aspects.
- Tactical thinking: An Online Professional Doctorate in Tourism Management enhances tactical thinking abilities, allowing individuals to recognize probable areas for development and transformation within the Destination Life Cycle Model.
- Innovative solutions: Graduates gain the competency to develop innovative solutions to intricate tourism predicaments faced by destinations at different stages of the life cycle.
- Leadership roles: A professional doctorate in tourism management prepares a graduate with the skills and aptitude to take on leadership roles in destination management, administering decision-making processes based on an in-depth understanding of the life cycle model.
In conclusion, the Destination Life Cycle Model is a valuable concrete framework for gaining a thorough understanding of the development of tourist destinations. It offers an insight into the various stages of destination transformation which include exploration, involvement, development, consolidation, stagnation, and rejuvenation. With the help of a Professional Doctorate in Tourism Management for Tourism professionals and by understanding and applying this model, destination managers and stakeholders can make informed decisions, address challenges, and take advantage of on opportunities to guarantee sustainable destination progression.
Leverage the proficiency of a Professional Doctorate in Tourism Management for the successful implementation of the Destination Life Cycle Model. Enroll for East Bridge College's Professional Doctorate in Tourism Management and embark on your journey towards leading destination transformation.
Written By : Rajosree Sur