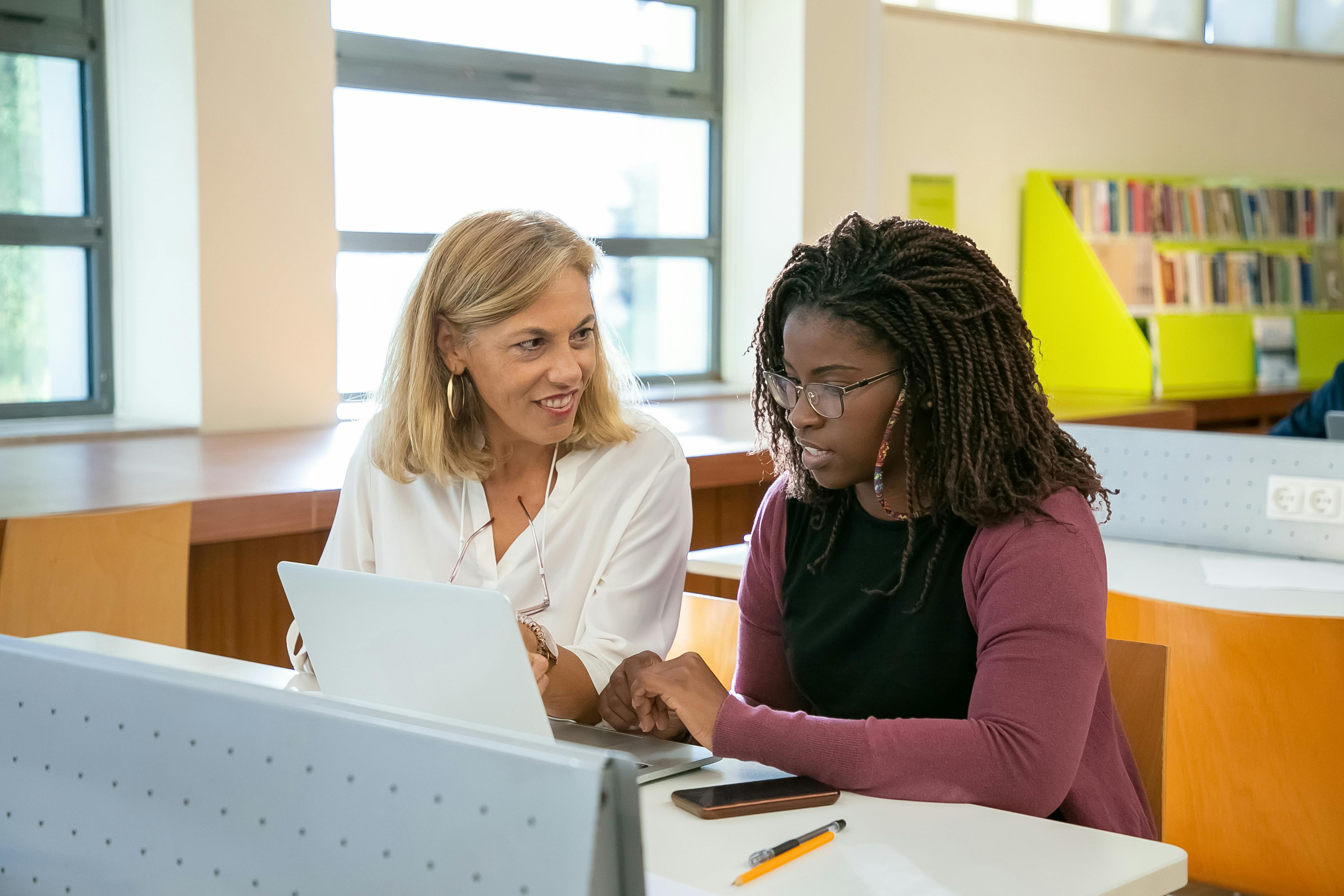
With the evolving educational landscape and the increased focus on engaging and intuitive learning, understanding students' psychological development has become imperative for educators worldwide. Educational Psychology is a branch of psychology that deals with the cognitive, emotional, and social development of children and how their learning environment shapes their educational growth. This field study is concerned with understanding how students learn and retain knowledge throughout their entire educational journey. Being equipped with the knowledge of psychological development in children and adolescents, educators gain a deeper understanding of the learning process of students and can guide them better in reaching their highest potential.
Over time, the focus has shifted from theoretical learning towards experiential learning where students are subjected to immersive learning environments and engaging curricula. People are increasingly acknowledging the fact that education is not just imparting knowledge, but it comprises understanding how students gain knowledge and addressing and meeting their specific needs. Moreover, with immersive educational practices students are better equipped to be successful in their lives as they are not just passively mugging up information but rather actively taking part in their learning journey. It provides students with the scope to explore their individual interests and follow their natural curiosities.
Educational psychology also aids in promoting social and emotional development in students. How children develop socially and emotionally in their early years impacts their future interactions, relationships, and emotional regulation. More and more scientific studies demonstrate that children who acquire strong emotional skills during their early years can better handle social situations as they grow older. Hence, educational psychology plays an important role in the development of emotional intelligence in children leading to their increased success academically as well as personally. Research has shown that students with higher emotional intelligence usually perform well in their academic studies. They show an interest in learning, actively participate in investigations, and enjoy both reading and writing. Integrating social-emotional learning into early education helps children cultivate self-awareness, self-regulation, and empathy. This leads to improved social skills, strong relationships, and a sense of belonging within social groups.
Why Master of Education (M.Ed.) with Educational Psychology?
Educational Psychology focuses on studying how individuals learn and developing more captivating and efficient curricula. A Master of Education degree specialising in Educational Psychology examines teaching methods, individual learning variances, and formulating effective teaching curriculums and strategies. The program equips teachers and educators to effectively navigate the modern educational landscape by imparting the knowledge of creating engaging curricula, conducting culturally diverse classroom teaching and devising innovative learning and teaching practices.
The course is ideally suited for professionals who are interested in delving deeper into how biological, social, and cognitive elements in children support their overall growth and influence their educational path. The online M.Ed. program in Educational Psychology at East Bridge University focuses on providing candidates with theoretical methods, research results, and scholarly works that emphasise the importance of psychology in education. The program helps professionals to specialise in child psychology, comprehending the different requirements and aspects of a child's psychological growth, and the significant role that early education plays in children's development.
An M.Ed. in Educational Psychology enables individuals to conduct in-depth research on human development theories, helping candidates gain a deeper understanding of the diverse learning journeys and create inclusive teaching methods that are both dynamic and comprehensive. Educational Psychology also deals with the theories and methodologies of the psychology of learning and teaching that provide educators with a robust understanding of the basic fundamentals of psychology. This academic knowledge coupled with practical exposure and modern innovative learning aids teachers in excelling in their teaching career. The study of educational psychology also helps participants understand the different social, cognitive, and emotional processes in learning and build classrooms that are welcoming to all.
Understanding Educational Psychology: Nature, Scope and Methodologies
Educational Psychology focuses on exploring how teaching and learning occur in formal settings, as well as finding methods to enhance these processes. It includes essential subjects such as learning theories, teaching strategies, motivation, cognitive, emotional, and moral growth, and parent-child interactions, among others.
The nature of Educational Psychology can be outlined in the following manners:
- Educational Psychology as a Scientific Study. Science can be defined as a field of research focused on observing facts and creating testable universal principles. Science uses specific, unbiased techniques to gather data. Its purposes include comprehending, elucidating, forecasting, and managing phenomena. Just like all other sciences, educational psychology has advanced objective techniques for gathering data. It also strives to comprehend, forecast, and manage human behaviour.
- Educational Psychology as a study of Natural Science. An educational psychologist collects data, conducts investigations, and draws conclusions in the same way as a physicist or biologist.
- Educational Psychology as a study of Social Sciences. Similar to sociologists, anthropologists, economists, and political scientists, educational psychologists analyse human beings and their interactions with society.
- Education Psychology as a study of Applied Sciences. Using psychological principles in the field of education is what it is all about. It aims to analyse the students' behaviour and experiences by utilising psychological principles and techniques. As a field of psychology, it is equivalent to other forms of applied psychology. Educational psychology relies heavily on information from developmental, clinical, and social psychology.
- Educational Psychology can be seen as a developing or growing science. It focuses on novel and continuously evolving studies. Educational psychologists gain a deeper understanding of children's characteristics and actions as they gather more research results.
Therefore, it can be said that Educational psychology is the study of practical, specific, social, positive, and applied science. While general science examines how individuals behave in different areas, educational psychology focuses solely on how individuals behave in educational settings. The field of educational psychology continues to expand as research in this area constantly evolves.
The following factors will determine the scope of educational psychology.
- The Learner: Educational psychology focuses on the learner as its central theme. Hence, understanding the students and the methods to understand them thoroughly are essential. The subjects cover the natural talents and skills of people, differences among individuals and how to measure them, the visible, hidden, aware, and unaware actions of the student, the qualities of their maturation process, and every phase from childhood to adulthood.
- The Learning Experiences: Educational Psychology assists in determining which learning experiences are beneficial, at which point in the learner's growth and development so that these experiences can be obtained more easily and enjoyably.
- Learning process: Once the learner is understood and the learning experiences are determined, Educational Psychology then explores the laws, principles, and theories of learning. Remembering and forgetting, perception, forming concepts, thinking and reasoning, solving problems, transferring learning, and effective learning strategies are other components of the learning process.
- Learning Situation or Environment: We focus on the environmental factors and learning situations that exist between the learner and the teacher. Subjects such as classroom atmosphere and teamwork, tools and methods that support learning and assessment, strategies and activities, counselling and guidance, etc. are essential for the effective operation of the teaching and learning process.
- The Teacher: The teacher plays a powerful role in any teaching and learning process. It explores the teacher's role. It stresses the importance of self-awareness for a teacher to fulfil their role in the educational process effectively. Anxiety, adaptation, goals, and more are important for understanding personality traits, interests, abilities, and effective teaching qualities to motivate one towards becoming a successful teacher.
Key Theories in Educational Psychology
- Behaviourism:
Key theorists in behaviourism include Edward Thorndike, Ivan Pavlov, John B. Watson, and B.F. Skinner. Behaviourism defines learning as an observable behavioural change in response to environmental stimuli. Positive and negative stimuli create associations that influence behaviour. Behaviourism emphasises external, scientifically measurable changes in response to stimuli, focusing on behaviour's learned causes.
Behaviourist theory emphasises classical and operative conditioning, focusing on reinforcing responses to stimuli. This reductionist approach breaks behaviours into parts for understanding. Behaviourism has influenced psychology and education, leading to behaviour modification and therapy. It shapes teaching methods by setting specific learning objectives and using reinforcement to guide learning.
- Cognitivism:
Key theorists in cognitive psychology include Jean Piaget, Jerome Bruner, Robert Mills Gagne, Marriner David Merill, Charles Reigeluth, and Roger Schank. Cognitive psychology emerged in the 1950s, focusing on human rationality and the complexities of the mind as it processes information. It emphasises learning as a result of mental activities, using the computer as a metaphor for the human mind. Cognitivists evaluate learning based on knowledge and understanding demonstrated by learners, rather than observable behaviors. They emphasise the importance of purposeful learning, focus, learner goals, and discovery of ideas to support whole-mind understanding.
Cognitive psychology focuses on the schematic and symbolic acquisition of knowledge, emphasising internal mental processes in learning. It stems from Piaget's stages of development and emphasises the role of experts in transmitting information while highlighting the learner's mental capacity and motivation.
- Constructivism:
Constructivism, introduced by key theorists John Dewey, Jean Piaget, Lev Vygotsky, and Jerome Bruner, challenges traditional views of learning. Learners construct their own knowledge through interpretation and restructuring, with teachers serving as guides rather than sources of information. Social constructivism emphasises social interactions in learning, while cognitive constructivism focuses on cognitive processing. Constructivism influences modern teaching methods, emphasising student-centred approaches like problem-solving and group work.
- Experientialism:
Experiential learning theory was developed in the 1970s by David A. Kolb and Carl Rogers, influenced by constructivism and social learning theories. It focuses on the importance of direct experience in learning, with learners actively participating in the process to enhance understanding and behaviour.
Maxwell emphasises the importance of experientialism to enhance learning by offering real-life experiences. Experientialists believe in creating nonthreatening learning environments for learners to experiment and engage freely. This approach influences educators' lesson planning and shapes theories of organisational learning. Schools incorporate experiential education through field trips, projects, internships, and study abroad programs.
- Social and Contextual:
Key theorists in social and contextual learning theories include Lev Vygotsky, Albert Bandura, Jean Lave, Barbara Rogoff, Etienne Wenger, and Thomas Sergiovanni. Emerging in the late 20th century, these theories focus on how the environment and social contexts shape one's learning, emphasizing interactions between individuals and situations.
Bandura's ideas align with Vygotsky's Zone of Proximal Development, emphasiing the role of interaction with knowledgeable mentors for learning. Lave and Wenger see diverse knowledge levels as beneficial for communities of practice, relying on cooperation and problem-solving for learning. Sergiovanni supports this approach for schools to improve.
Benefits of Educational Psychology
- Developing Effective Teaching and Learning Strategies: Educational Psychology uses psychological ideas, theories, models, and concepts in motivation, working memory, thinking, problem-solving, growth and development, and intelligence. These subjects allow them to choose a psychological principle application that fits the school setting, the traits of the instructor, and the students. Recognising the primary elements that affect the calibre of instruction will help teachers plan and execute efficient problem-solving techniques.
- Opting for the Best Learning Methods: The needs of the student are the foundation of learning strategies. In addition to relating to the traits and individuality of each student, educational psychology can assist teachers in identifying the most effective teaching and learning strategy or method - the different learning styles and types, as well as the student's developmental stage. Selecting the most effective teaching techniques and strategies requires a thorough understanding of the students.
- Recognising Individual Differences: Education must include an understanding of individual differences. To effectively instruct students, teachers must be aware of their unique needs and characteristics at different levels. Additionally, knowing the various traits of students enables teachers to establish a learning environment. Teachers and aspiring educators can use it to better understand the traits of children at different developmental stages and adjust their teaching methods accordingly. Teachers can raise their students' grades by employing strategies that take into account their differences.
- Understanding What Matters: Anything that is incorrect about the educational and learning process is excluded from educational psychology. It focuses on what matters when discussing teaching and learning. It gives teachers the most crucial knowledge and abilities. These do not include any theories or points of view that are based on subjective and erroneous observations about students or on personal opinions. Teachers are also better able to comprehend each student's needs and the type of education that will work best for them.
- Creating an Environment That Is Good for Learning: It is crucial to assist educators in creating an appropriate learning environment. For the learning process to be successful, teachers must be able to establish a positive emotional environment in the classroom. A teacher needs to be aware of the features of the classroom setting. Instructors must be aware of the type of learning environment they hope to establish in the classroom. Teachers must understand the fundamentals of education and learning as well as alternative methods for facilitating learning. It is crucial to assist educators in creating a learning-friendly environment in the classroom.
- Providing Proper Guidance: To support each student's success, teachers must be aware of their individual needs. Teachers should assist students in overcoming challenges as they progress through the learning process. Students at various stages of life require educational and career guidance. It aids educators in knowing what pupils should learn and how to best instruct them. Additionally, it assists educators in recognising and resolving any problems that might impede learning.
- Assessing Learning Outcomes: Since a variety of factors affect a student's success, evaluation is a challenging task. It assists teachers in examining the connection between student achievement and teacher behaviour in order to gauge student learning. It assists them in determining the most effective methods of evaluating student learning and in creating assessments that fairly represent the knowledge and abilities that students ought to have upon finishing a course. It supports educators in lesson planning, student progress evaluation, and teaching efficacy assessment.
Career Opportunities after M.Ed. with Educational Psychology
Educational Psychology is a specialised field in education that enables professionals to opt for traditional teaching roles as well as newer teaching jobs such as student counselling, career guidance, special child education, online mentoring and so on. A master's degree in Educational Psychology enables candidates to work in elementary and secondary schools, as well as, colleges, universities and professional educational institutions.
Educational Psychology equips candidates with the knowledge and skillsets required to develop engaging curricula, conduct sessions in culturally diverse classrooms, carry out interactive classroom sessions, and develop innovative teaching and learning strategies.
Some of the roles best suited after completing a Master of Education with Educational Psychology:
- Researcher
- Professor
- Educational Mentor
- School Administrator
- Special Educator
- Program Mentor
- Educational Counsellor
- Child Counsellor
- Teacher
- Instructional and Curriculum Designer
- Teacher Trainer
Concluding Thoughts
Educational psychology is a specialised branch of study that amalgamates education and psychology to better understand students, their needs and aspirations, and their learning processes. It is a field of study that is gaining popularity due to the increased focus on intuitive, interactive and engaging learning as compared to traditional systems of imparting education. The study of Educational Psychology focuses on theoretical concepts as well as real-life practices that enable professionals to seamlessly navigate the modern educational landscape.
Opt for an online M.Ed. degree with a specialisation in Educational Psychology from East Bridge University that comes with the flexibility of time and the ability to pursue the course from anywhere in the world. Enhance your teaching career with a specialised degree in Educational Psychology driving positive changes in the education sphere.
Written By : Tammy C. Bow